Websites can pose many risks for consumers, especially for those who share private and privileged information through them.
- Social security numbers.
- Credit card information.
- Bank routing details.
- Home addresses.
They’re taking a huge risk inputting that information into your WordPress website, so you better have a way to keep that information safe.
Typically, when we look at the most common security vulnerabilities, the same recommendations are made over and over again to help users fortify their websites. One of the tools most frequently recommended for this?
The SSL certificate.
What is an SSL Certificate?
SSL stands for “Secure Sockets Layer”. Basically, what that means is there is a layer of encryption placed between a web server and someone trying to access content on it.
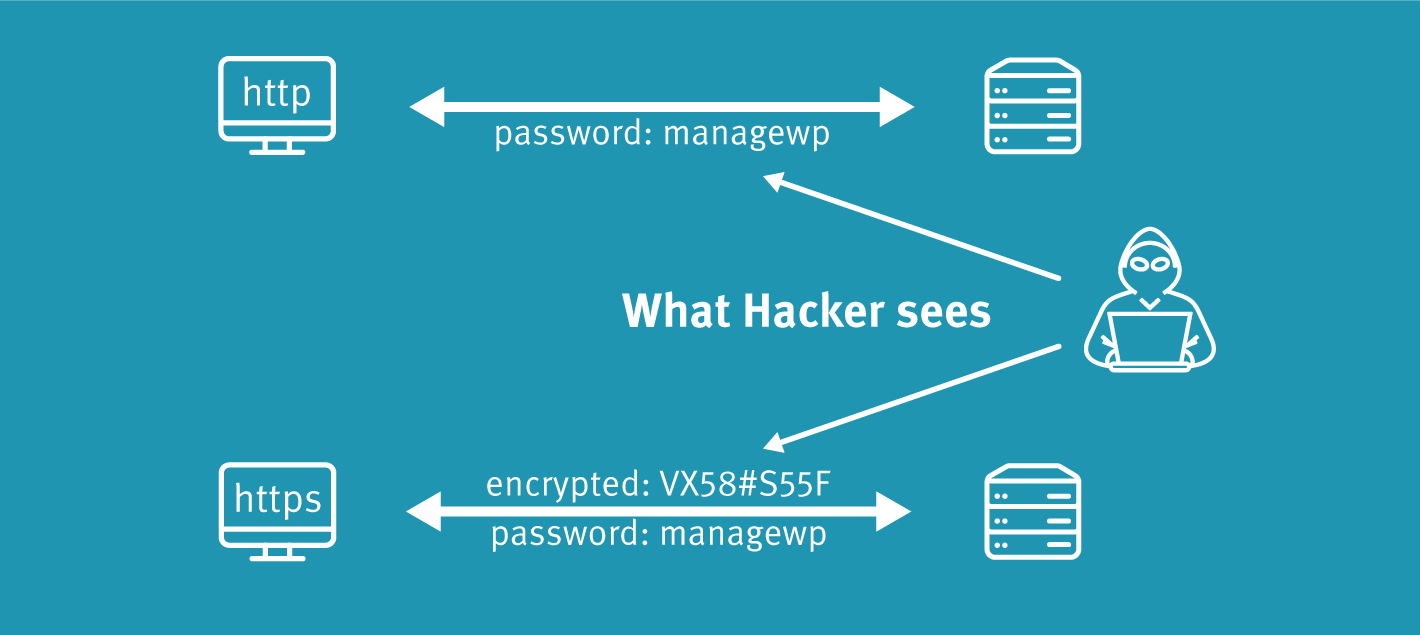
At its core, an SSL certificate is encryption for web servers. It protects the exchange of information that takes place between a server and a user by utilizing a set of cryptographic keys: one public and one private.
A public key is what encrypts your message and a private key is what decrypts it. This is how your users’ information is kept hidden from prying eyes.
Once a user’s browser verifies that your website has a digitally signed acknowledgment of an SSL certificate, their encrypted session will begin. They’ll, of course, never actually see this exchange take place, but there are certain indicators and trust marks that let them know when a secure communication between your server and their website is taking place.
How Do You Know an SSL Certificate Is Present?
There are various indicators used in browser address bars that let users know when there is an SSL certificate installed.
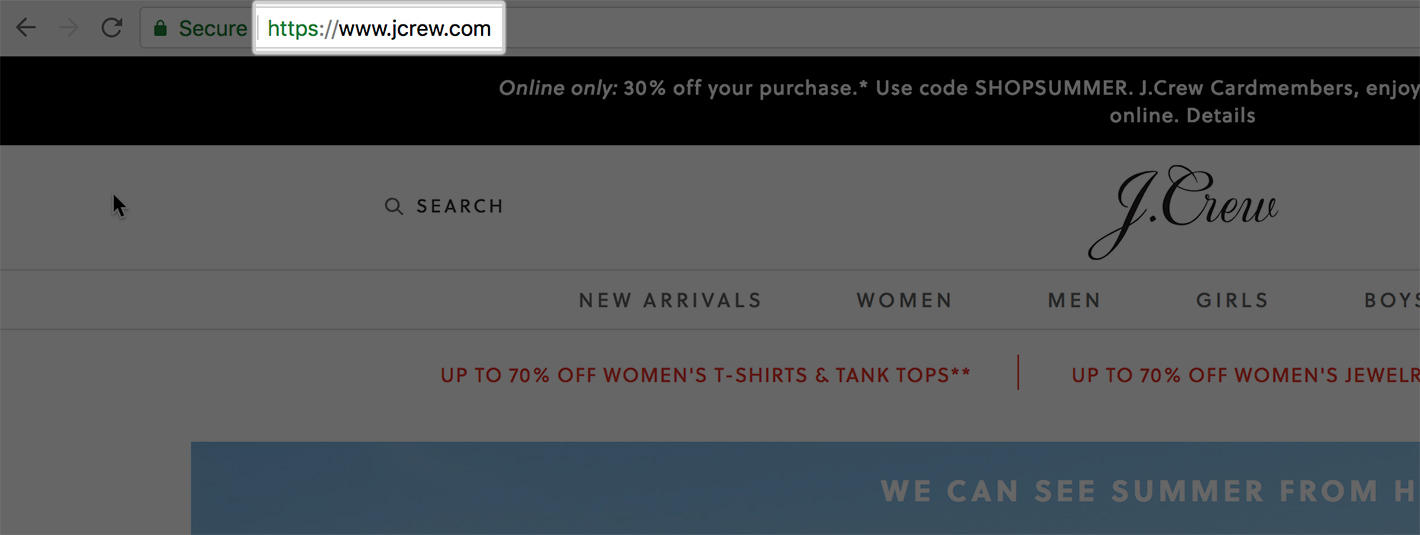
The first is the actual web address. All websites with an SSL certificate will start with “https://” (as opposed to the old “http”).
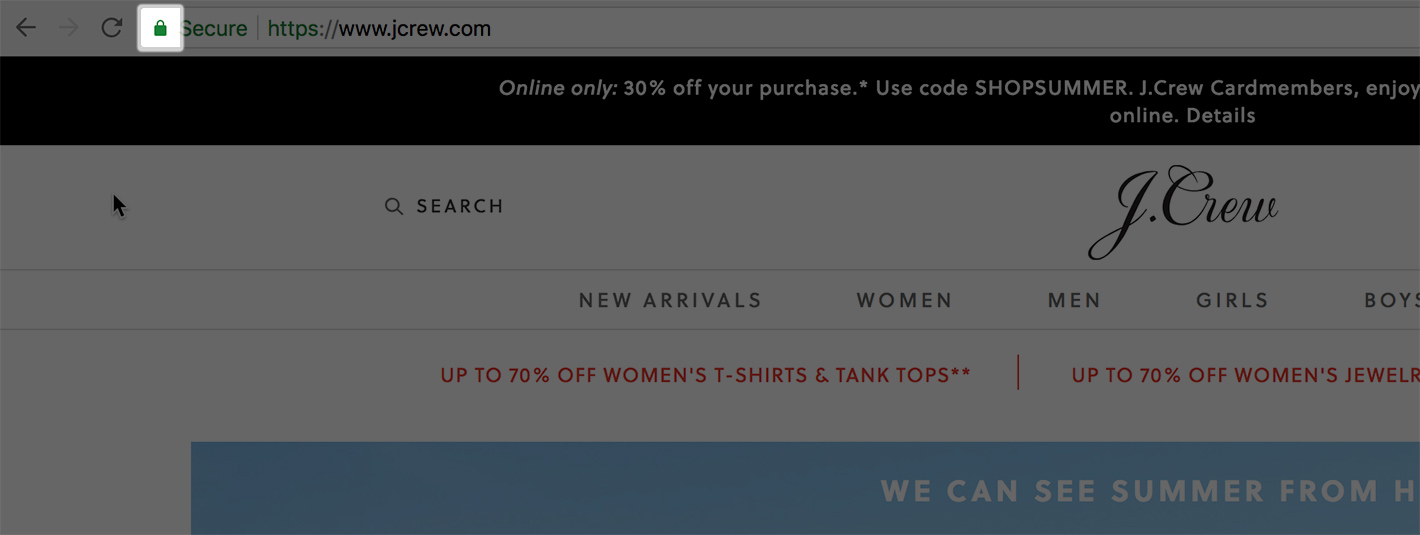
The second is the padlock symbol. It will be on the left side of the address bar.
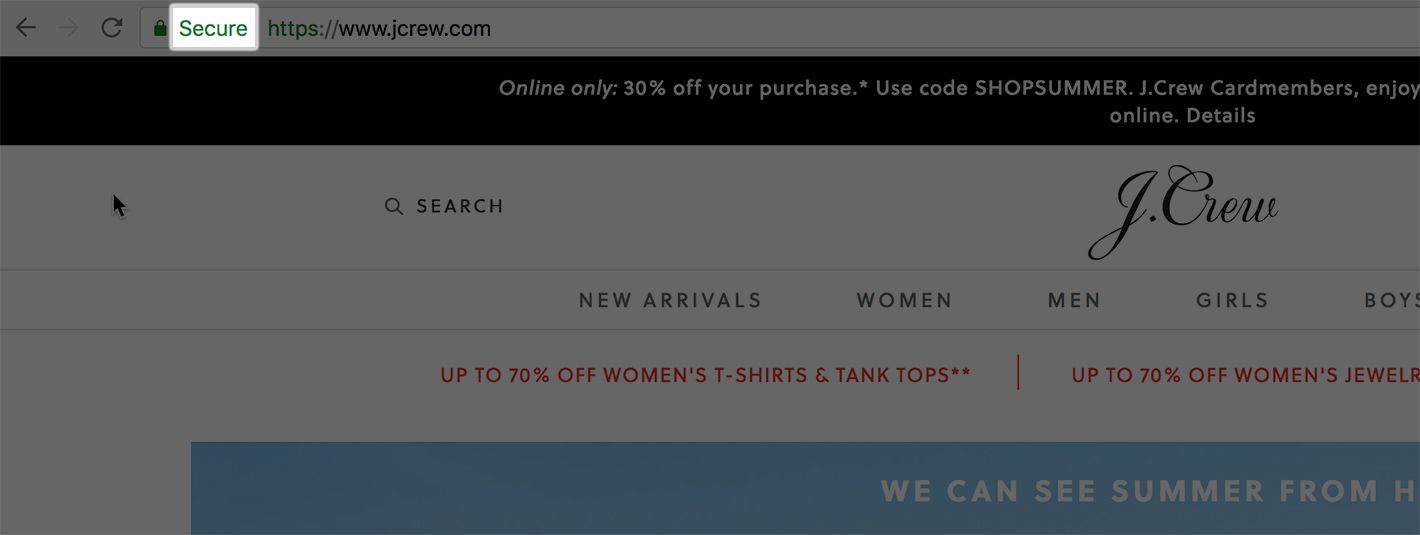
Now, the two SSL certificate indicators above are pretty standard across most browsers. However, for anyone using Chrome, they have the added bonus of being shown a “Secure” message with certain levels of encryption.
Currently, Chrome displays a red “Not Secure” message in the address bar only for websites that collect information through contact forms or e-commerce checkouts. Beginning in July 2018, that will change (more on that below). For now, websites that remain without an SSL certificate and on HTTP will see the “i” icon:

The message below the icon is what visitors will find when they inspect the address for an SSL certificate. On the other hand, for websites that do have one, they’ll find further details about security, like this:
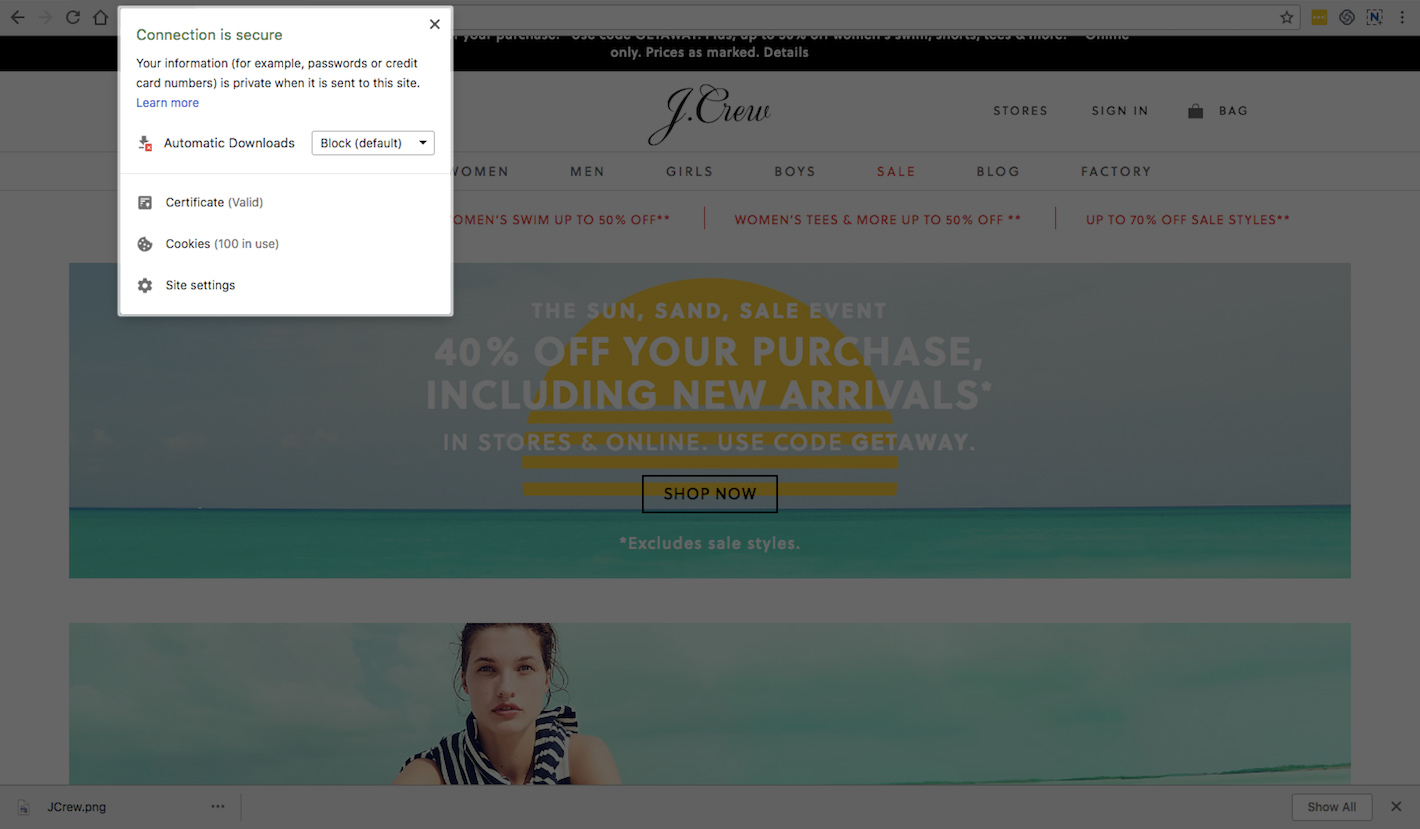
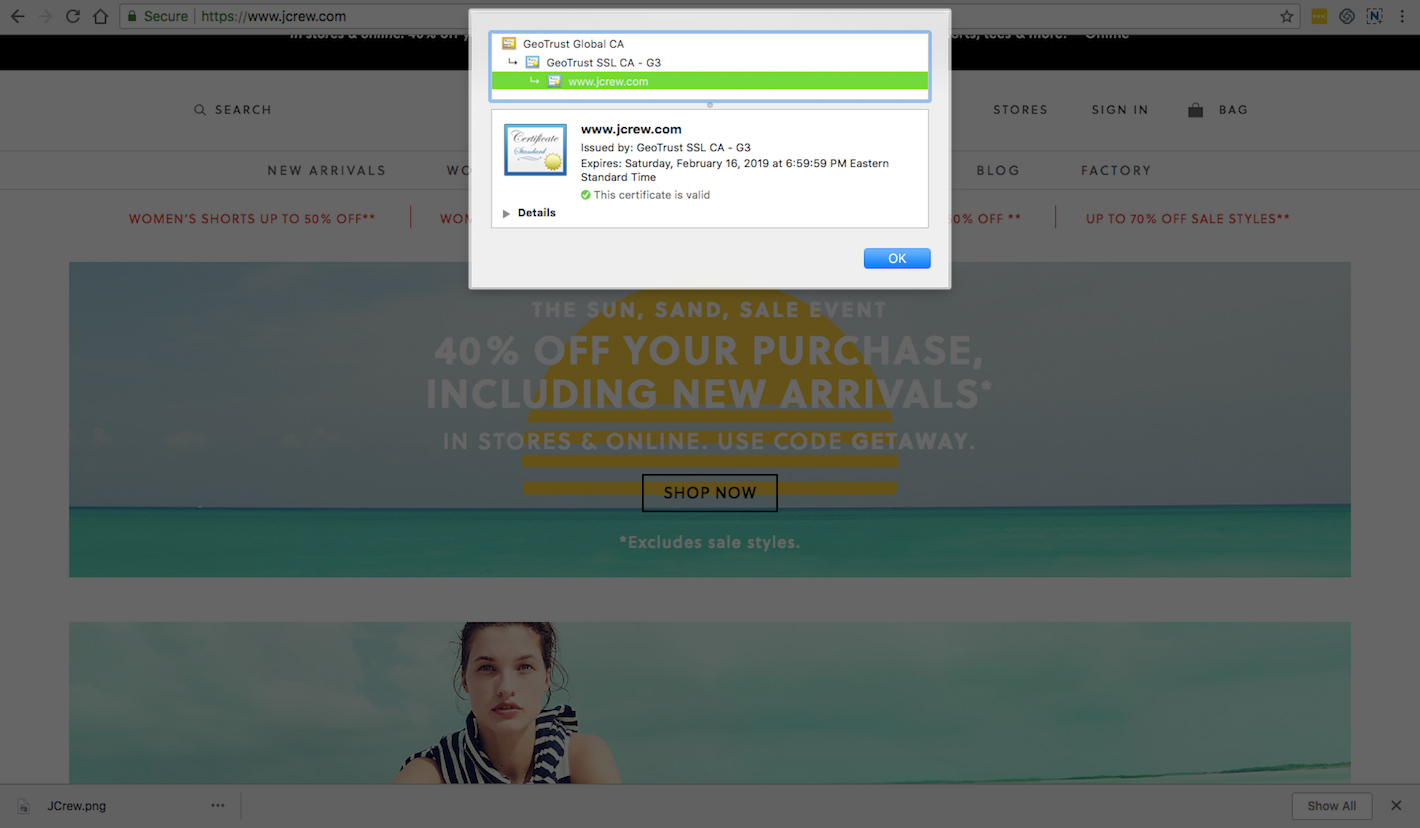
And if they click on “Certificate”, they’ll uncover details about the website’s actual SSL certificate, the owner of it, as well as the Certificate Authority (CA) that issued the secure encryption.
With this sort of blatant “secure” and “unsecure” notification presented by Google and other browsers, your visitors are assured that it’s safe enough to share their data with your website.
Why Does Your Website Need an SSL Certificate?
Google’s mission to make the web a more secure place has been going on for awhile.
Back in 2014, it began to really put its weight behind the SSL certificate when it announced that HTTPS would become a ranking signal. At the time, it was only a gentle push Google was giving its users.
In 2016, Google took additional steps to get the SSL certificate in place with more websites. This is when it introduced the “Not Secure” penalty to websites that processed passwords and credit card data over an unencrypted server.
Starting in July 2018, Google now decrees that any website without an SSL certificate will be marked as “Not Secure”. While this was originally meant to be a penalty for websites handling sensitive information, Google now believes that all websites should be more responsible in providing secure online experiences.
Interestingly enough, Google is actually going to remove the green “Secure” label from Chrome beginning in September. As Product Manager for Chrome Security, Emily Schechter, explained:
“Users should expect that the web is safe by default, and they’ll be warned when there’s an issue. Since we’ll soon start marking all HTTP pages as ‘not secure’, we’ll step towards removing Chrome’s positive security indicators so that the default unmarked state is secure.”
8 Great Benefits of SSL Certificates and HTTPS
So, besides getting one because Google says you should, why else might you want your WordPress website to have an SSL certificate? Here are 8 reasons:
- It’s safer for you and your visitors. Any good security plan will include an SSL certificate.
- Without one, your website will display a red “Not Secure” warning, which is not a good look for anyone.
- Having verified proof you’ve put a security measure in place for visitors can do wonders for boosting trust in your brand (and, subsequently, conversions).
- Some SSL certificate providers give you additional trust marks to place on your website (like Symantec placing the Norton security seal at checkout).
- Because an SSL certificate publishes information about the domain owner and, sometimes, the corporation behind it, this gives your brand more credibility.
- Google uses SSL certificates as a strong ranking signal now.
- Using an SSL certificate when the competition doesn’t will give you a clear advantage in the customer’s’ eyes.
- e-Commerce websites that use SSL certificates are abiding by PCI compliance guidelines.
When Should You Use an SSL Certificate?
For a while, Google was really only targeting e-commerce websites and those collecting sensitive data from customers. Then, it began targeting anyone with a contact form. Now, the rule is that everyone needs to have an SSL certificate on their website.
Granted, this is only a suggestion coming from Google, which means that the “penalty” noted above only occurs when visitors come to your site through the Chrome browser. That said, Chrome is the most popular browser and has been for awhile.
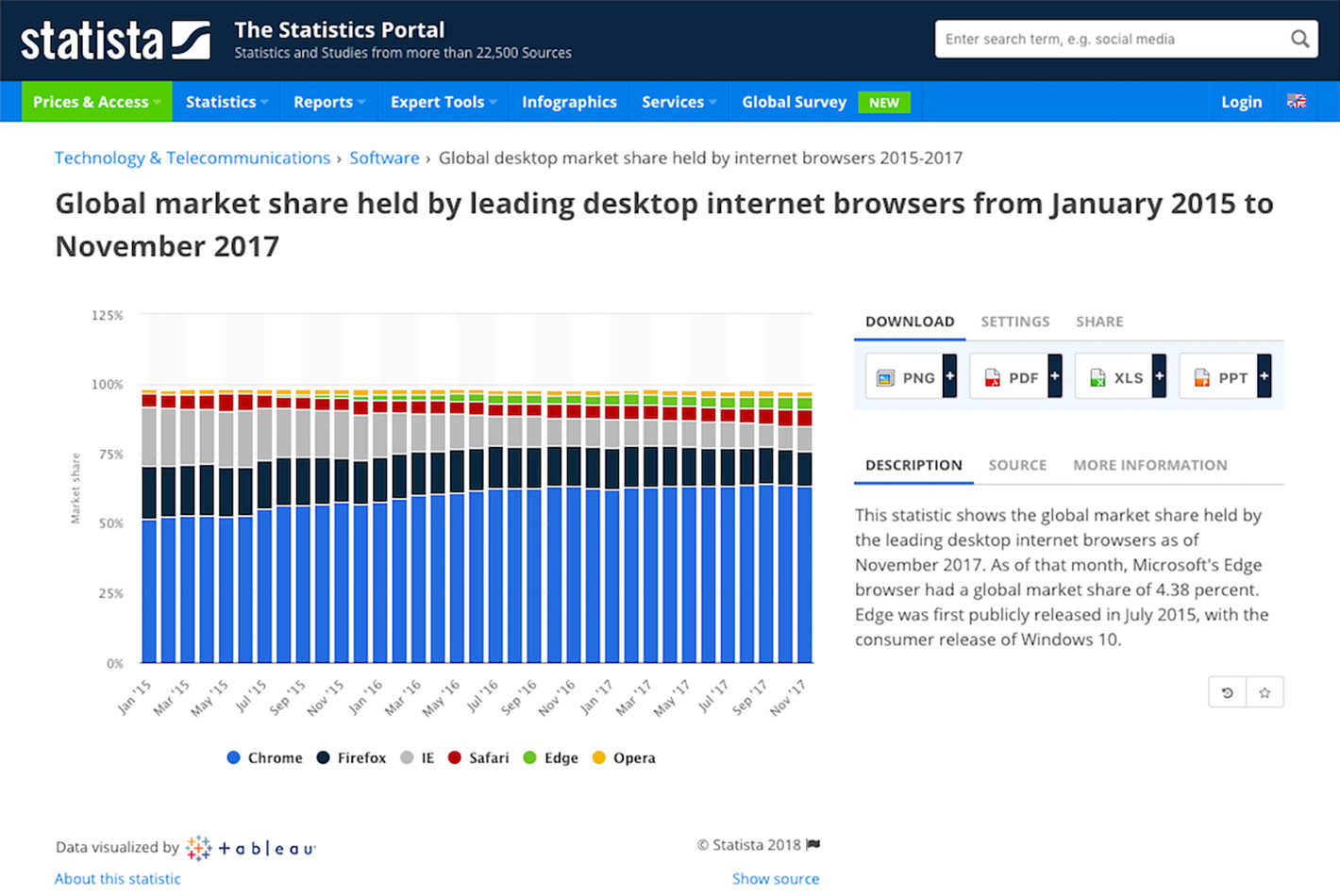
Unless your analytics tell you that your visitors don’t use Chrome, not getting an SSL certificate could be a risky move. So, do yourself a favor, and get one.
A Final Note
I’m very happy that Google is giving everyone a strong push towards creating a more secure web by using SSL certificates.
That said, this can’t be the only form of security you implement on your WordPress site. Firewalls, malware scanners, DDoS protection, spam blockers, and more need to be used to keep you and your users safe. You also should have a security checker that watches over your website and makes sure nothing slips past security. Only then will your website be safe.
Now that you know all about the why you should use SSL certificates, you need to learn about how to get an SSL certificate and install it on your WordPress website.

Leave a Reply