Your website is always evolving and publishing newer, better content to replace outdated posts. However, it can be tricky to avoid 404 errors and retain your page rankings when removing old content.
That’s where redirection comes in. This process sends your visitors to your new, live content when they try to access posts you’ve moved or deleted, reducing 404 errors. They also help pass on your old page rank to your updated articles.
In this article, we’ll discuss the importance of redirects and how you can set them up. We’ll then look at some best practices and tips to help you get the most out of yours. Let’s get started!
Understanding the importance of redirects
Redirects, when used correctly, can be very beneficial to your website. The internet is constantly changing, and your site’s content and structure sometimes have to adapt along with it.
However, if you delete a page or move it to a new URL, visitors will see a 404 error when they try to reach it at its old address:
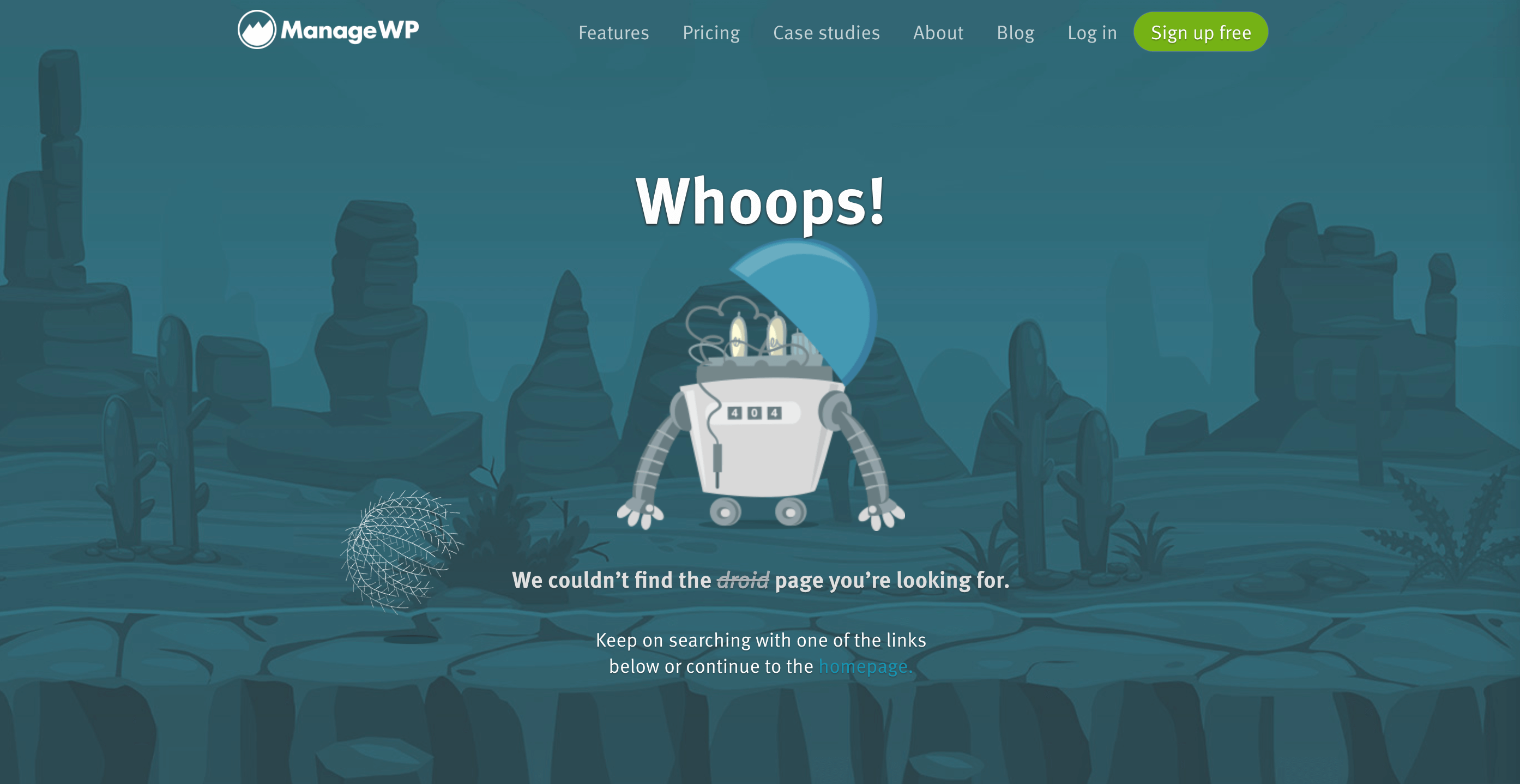
Even harmless errors like this one can make your site seem less professional and confuse visitors. Broken links also make it harder for users to find their way around your site.
WordPress redirection is similar to updating your mailing address with the post office. When a visitor types the URL for a redirected page into their browser, they’re forwarded to the page’s new URL. The same thing happens if they click on a link to the old address – they’ll simply be sent to the new one automatically.
Additionally, redirection can pass the Search Engine Optimization (SEO) benefits of your old page on to your new content. This is especially important for maintaining the authority lent to your site by backlinks.
There are three types of redirects. 301 redirects are the most common and indicate the page has permanently moved. A 302 redirect tells browsers the page was found at a different location than the one specified, and is usually used for temporary redirects.
It is also possible to use a 307 redirect for temporary moves if you’re planning to go back to the old address in the future.
You can manually set up redirects in your .htaccess file. However, it may be simpler to use a WordPress plugin such as Redirection. It enables you to easily enter the URL of your old page and the address of the new one.
6 WordPress redirection tips and best practices
Using WordPress redirection can seem easy when you start, but there is a lot that could go wrong. Knowing some best practices can help you set them up correctly. Here are six tips to start you off on the right foot.
1. Use 301 redirects (most of the time)
As we have stated, there are a few types of redirects that you can use on your website. Implementing the wrong one can cause issues for your website’s SEO. Fortunately, it’s easy enough to remember which type to use, since the answer is almost always a 301 redirect.
301 redirects indicate permanent page moves. When search engines see these redirects, they know to pass the SEO value of the old page to the new one. This can help you retain your position in search results.
Search engines will also de-index the original URL indicated by a 301 redirect after a certain period of time. That way, visitors will see and click on the listing for your new page instead of having to be forwarded there from the old one.
302 and 307 redirects will still send your visitor to the right page. However, search engines will perceive the move as temporary. This results in the SEO value staying with the original URL. You’ll have to optimize your updated content from scratch.
Additionally, the old page will stay indexed. Having duplicate content indexed by search engines can result in you fighting yourself for a higher position on results pages.
2. Redirect to relevant pages
The purpose of redirects is to avoid 404 errors when you delete or move content. While this is important, it’s not helpful if you redirect visitors to an irrelevant page. This can increase your bounce rate and negatively impact your SEO.
For example, say you have a dog accessory e-commerce website. If you stop selling a specific type of leash with no intention of selling it again in the future, you’ll likely delete its product page from your site.
Redirecting customers trying to reach the deleted product to a page for dog bowls isn’t helpful. They’re looking for leashes, so chances are they’ll leave your site. Instead, you should redirect them to a different leash they might be interested in.
You can apply this concept to any type of content.
3. Check that your redirects work
After setting up a redirect, you should check that it works correctly. Something as simple as a typo in your target URL could result in a 404 error, defeating the purpose of creating a redirect in the first place.
To check your redirect, you simply need to enter your old URL into your web browser. You should land on the correct destination page. If not, you’ll need to go back to your .htaccess file or the Redirection plugin to look for mistakes.
Additionally, if you use ManageWP, you can take advantage of our Link Monitor:
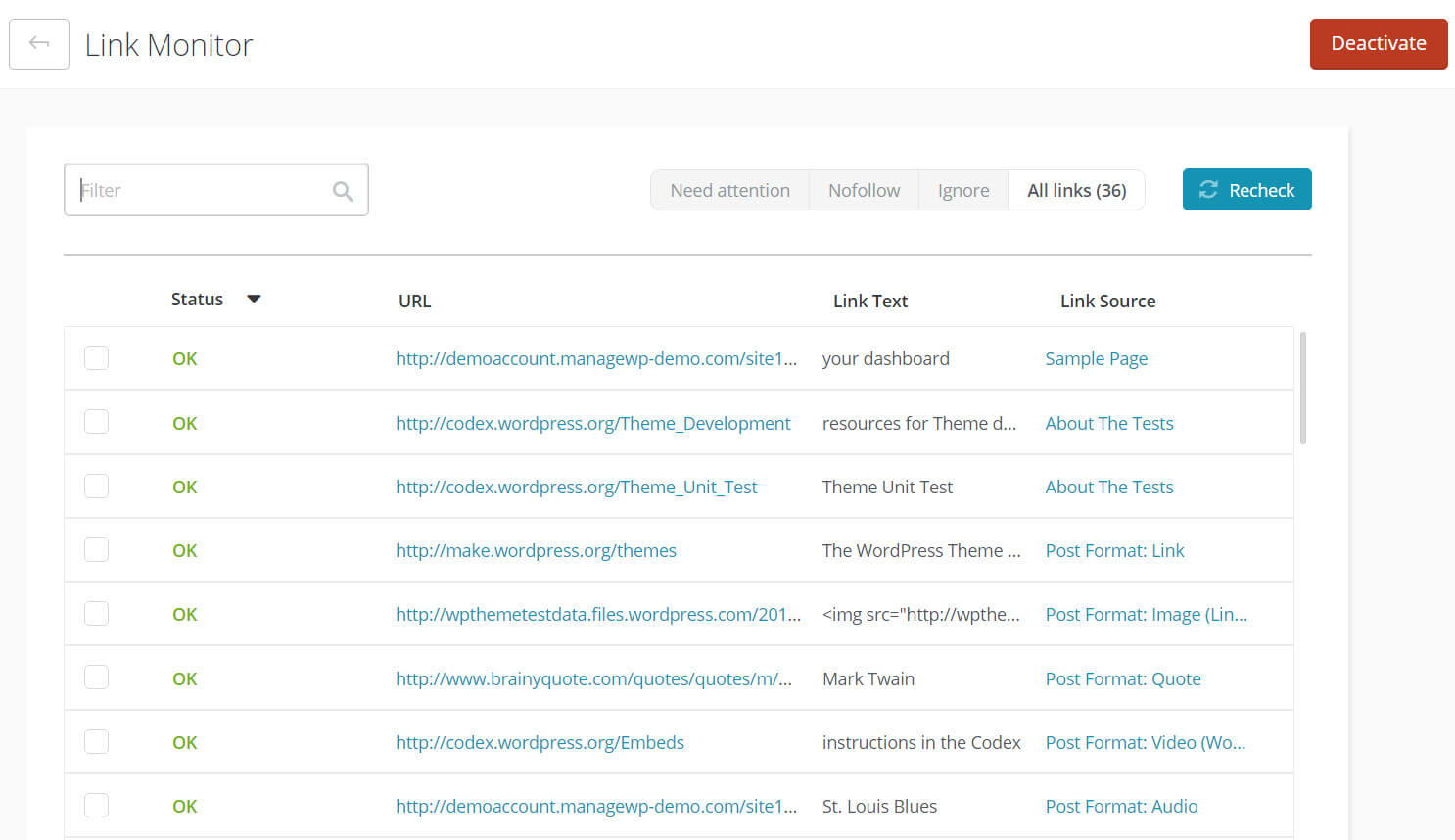
It will run through the links on your website daily and flag any that are broken. This can make it easy to spot unsuccessful redirects, as any links to pages you’ve moved or deleted will be highlighted.
4. Avoid redirect chains
As your website grows, you are likely to have more redirects. This can lead to redirect chains, which occur when you forward users from URL A to URL B, but URL B redirects to URL C.
While this might not seem like a problem, each new redirect adds a request to your server, slowing the speed of your page. This can negatively impact your SEO. Plus, visitors may leave your website if it takes too long to load.
If you’re using the WordPress Redirection plugin, you can check for redirect chains simply by looking at your list of redirects:
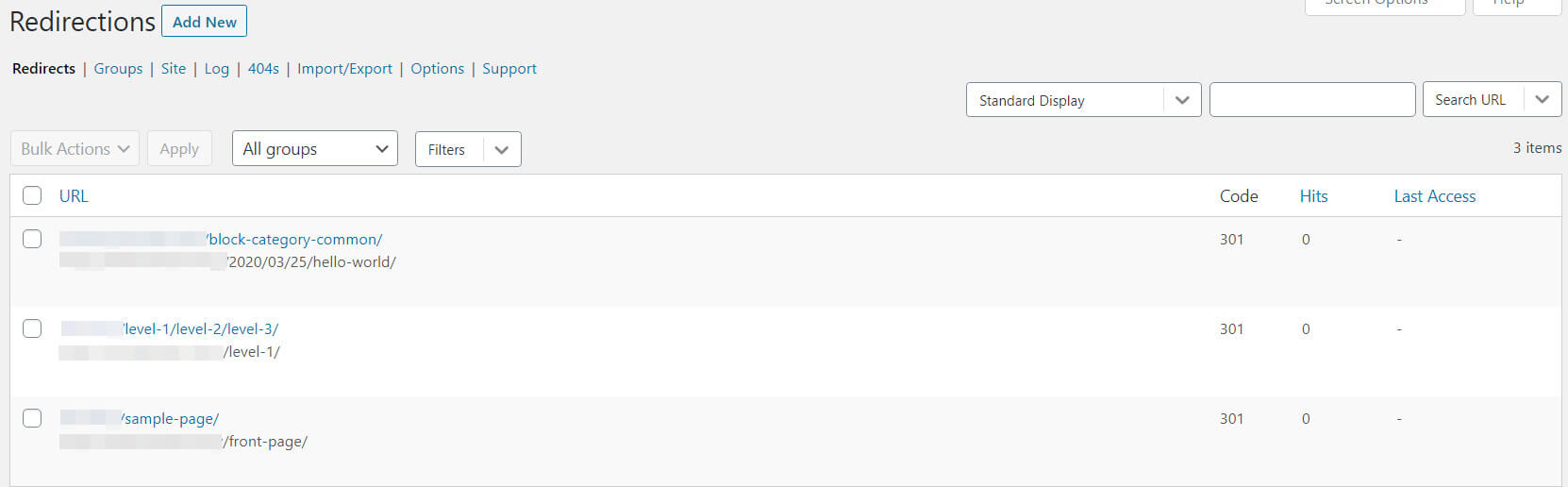
Search for your target URL. If it redirects to another page, you should use the final destination as your target instead.
5. Keep all redirects neat and tidy
Redirect chains are not the only issue you could face with a large website. As your number of redirects increases, they can become hard to navigate. This will also make it harder to track any redirect chains and to remove old redirects (which we’ll discuss shortly).
Using the Redirection plugin, keeping your redirects neat and tidy is easy enough with some basic housekeeping. The easiest way to manage them is to sort them into groups:
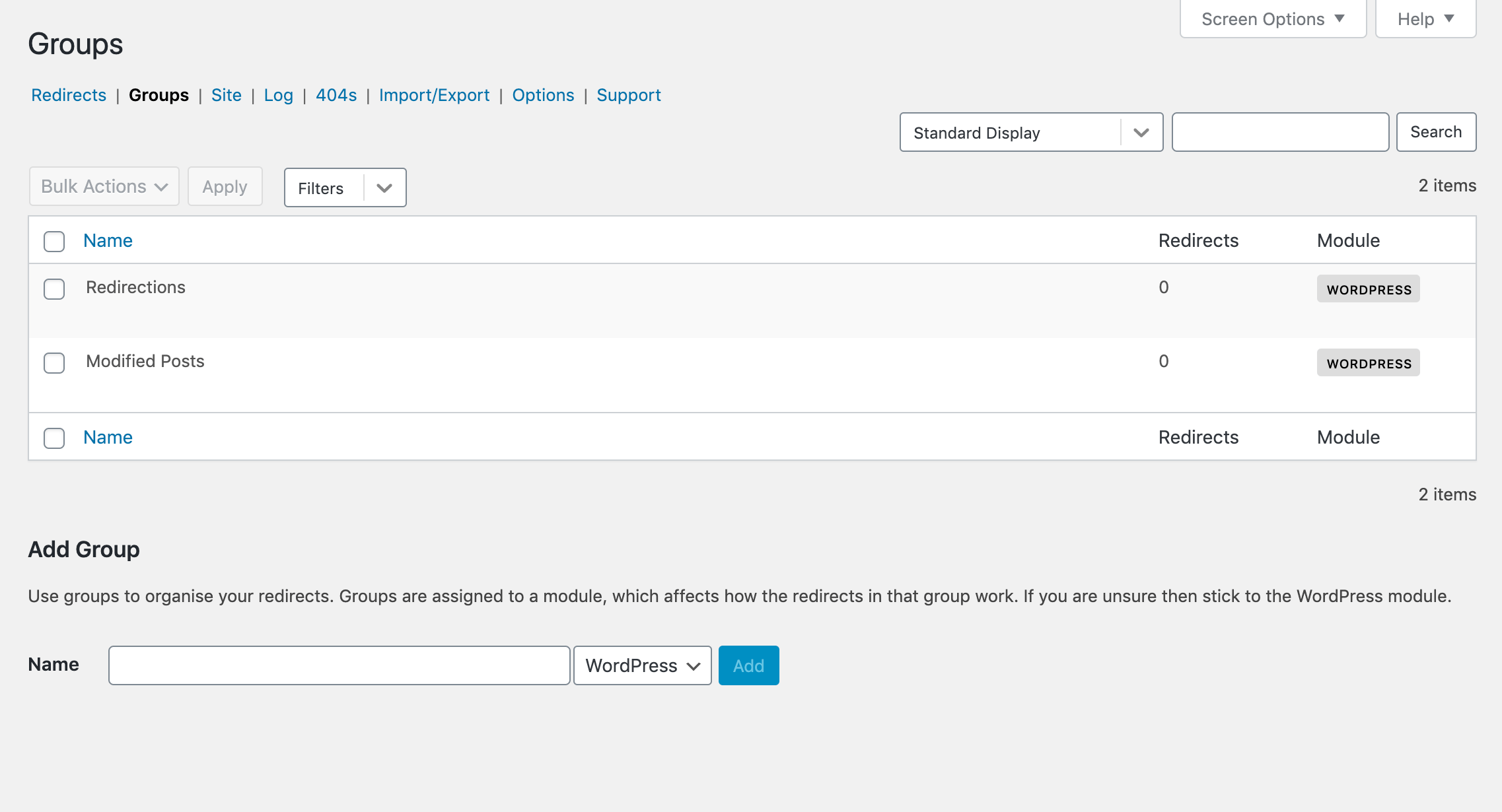
By categorizing your redirects, you can easily navigate to the relevant group any time you need to look for or otherwise manage a specific redirect.
6. Remove old 301 redirects
301 redirects should not remain on your website indefinitely. Over time, you should be able to remove them as search engine results, links, and other references to the original URL become updated with the page’s new address.
According to John Mu at Google, you should wait at least a year before looking into your old 301 redirects. At this point, you can check if the old URL is still receiving hits.
If there is no traffic to the old URL, you can remove the 301 redirect. However, if there is traffic, you need to leave it in place or you could face SEO problems.
You can easily remove an old 301 redirect using the Redirection plugin. All you need to do is find it in the list and click on Delete:
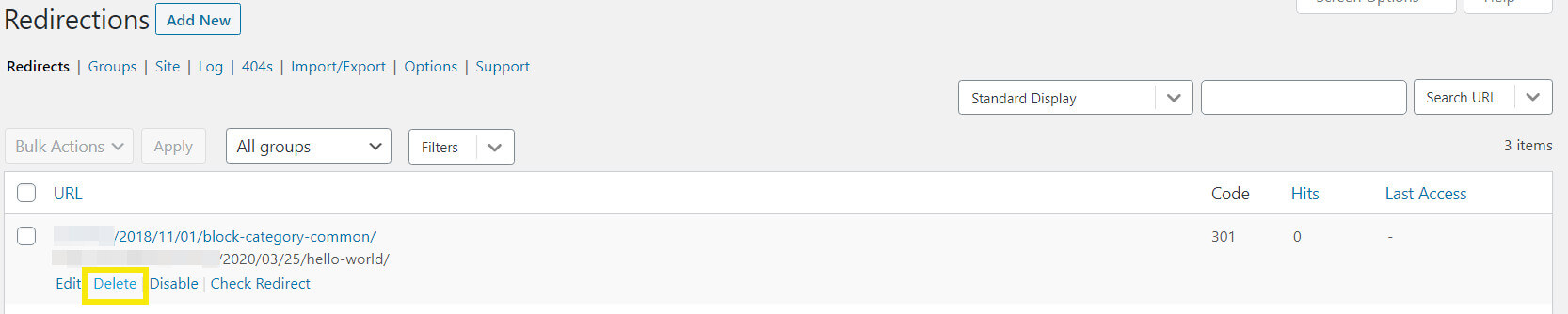
If you have manually added your redirects, you will need to remove the relevant code from your .htaccess file. This needs to be done with care to ensure you do not delete the wrong one.
Conclusion
Redirects are invaluable for making sure your visitors get to the content they want to see. When used correctly, they help you present live content instead of 404 errors, providing better User Experience (UX) while retaining your page rank.
To get the most out of your redirects, remember to:
- Use 301 redirects most of the time.
- Redirect to relevant pages.
- Check that your redirects work.
- Avoid redirect chains.
- Keep all redirects neat and tidy.
- Remove old 301 redirects.
Do you have any questions about redirects or best practices to share? Let us know in the comments section below!
Featured Image credit: Isaque Pereira.

Leave a Reply